Block Editor
The block editor field creates an isolated standalone Gutenberg block editor in meta boxes, settings pages, and other supported Meta Box objects. This is useful when you want to create a custom field for users to edit content with the same experience as the main WordPress block editor.
You can have multiple block editor fields on a same page, and they will not affect each other. Each editor can have a different set of allowed blocks, which is useful when you want to allow users to insert only certain blocks in a specific area of the page.
Screenshots
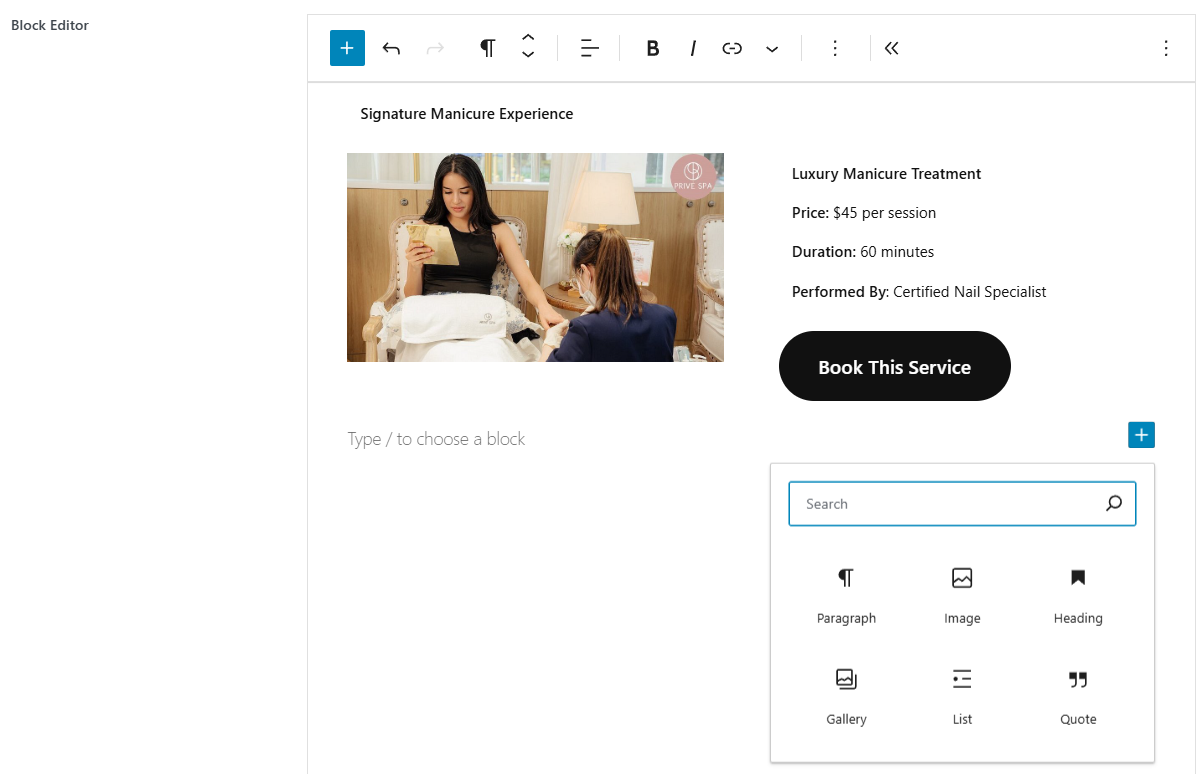
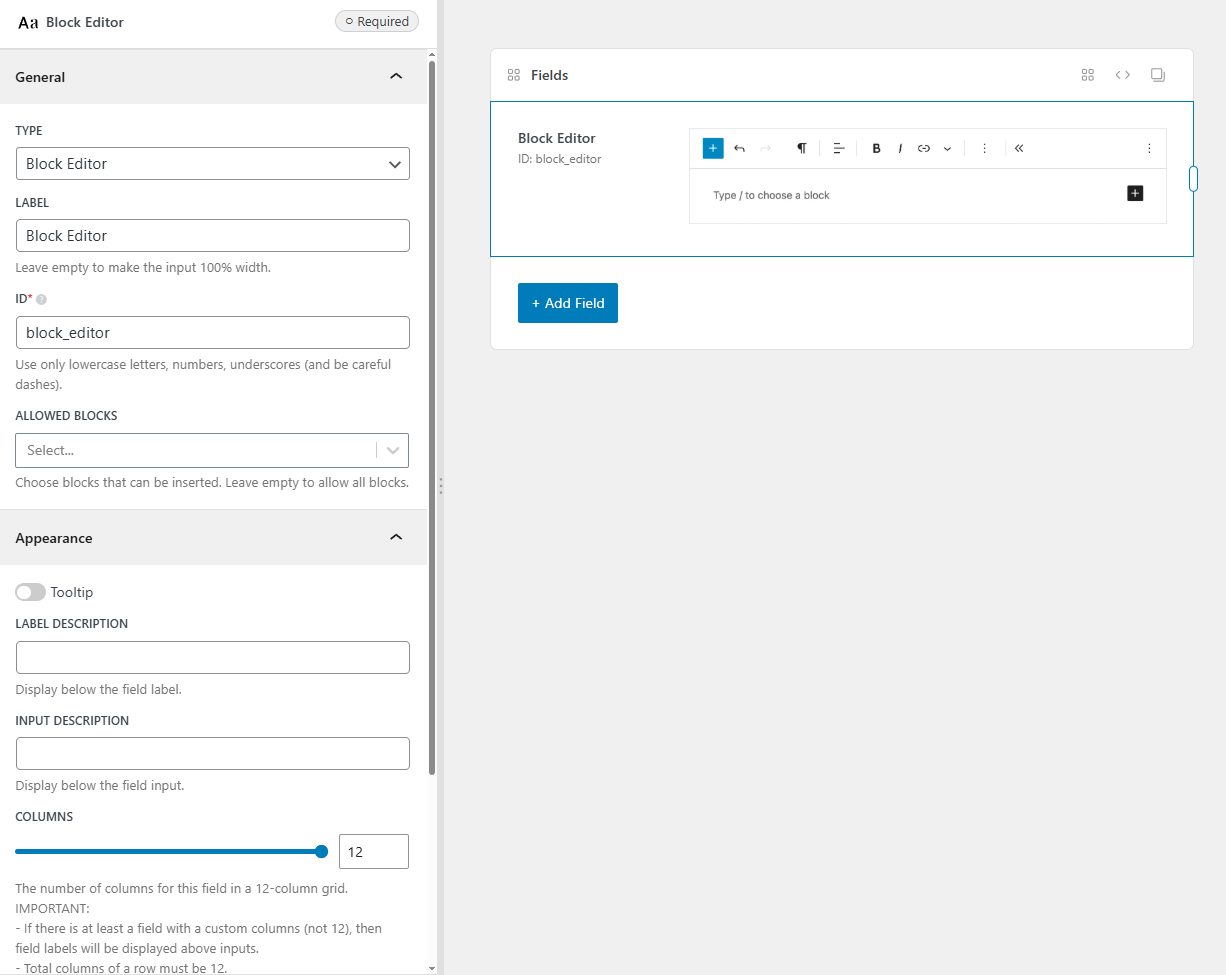
Settings
Besides the common settings, this field has a specific setting, the key is for use with code:
| Name | Key | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Allowed Blocks | allowed_blocks | List of allowed block types. Leave empty to allow all blocks. |
This is a sample field settings array when creating this field with code:
[
'name' => 'Content Blocks',
'id' => 'content_blocks',
'type' => 'block_editor',
'allowed_blocks' => [
'core/heading',
'core/columns',
'core/image',
],
]
Data
This field saves data as Gutenberg block markup in the database, just like WordPress stores blocks in post_content.
Displaying the value
Meta Box automatically applies do_blocks() when rendering the field value.
rwmb_the_value( 'content_blocks' );
If you want to get the value as a string, and apply do_blocks() to it, you can use:
$content = rwmb_get_value( 'content_blocks' );
echo do_blocks( $content );